Autonomous Decentralized Multi-Legged Robot System
(Prof.
H. YUASA and Prof. T. ARAI)
Bifurcation of Waves on a Graph (MPEG-1 Movie)
Fault-Tolerance Algorithm Simulation (before Failure) (after Failure) (MPEG-1 Movie)
Simulation of Hexapodal Robot (MPEG-1 Movie)
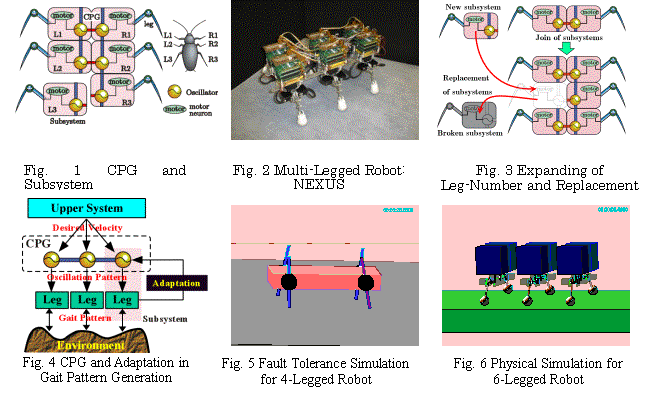
In this research, we have developed an autonomous decentralized multi-legged robot system (ADMRS, Fig.2). This system is modeled on the walk pattern generating mechanism of walking animals (Central Pattern Generator: CPG, Fig.1). Each leg is an autonomous partial system (subsystem) and communicates with neighbor subsystems, and then harmonious gait patterns are achieved as the total system. ADMRS can be composed of any number of legs and has the features such as high fault-tolerance and easiness of maintenance (Fig.3).
We developed the mathematical CPG model suitable for ADMRS. The model generates natural oscillating modes and makes them transit according to the oscillation energy. The modes and the energy correspond to the gait patterns and the desired walk speed respectively. Thereby, this model can generate and transit the gait patterns according to the number of legs.
Moreover, we research the environment adaptation algorithms for ADMRS (Fig.4). They modulate the gait patterns to the changes of the environment and the robot structure. We have proposed the fault-tolerance algorithm as one of them. This algorithm evaluates the leg failure by the energy consumption change and changes the gait patterns so as to distribute the energy change. The effectiveness of the algorithm was verified on the physical simulation (Fig.5, 6).
Keywords: Autonomous Decentralized System, Multi-Legged Robot, CPG, Gait, Fault-Tolerance
References
Shinkichi Inagaki, Hideo Yuasa, Tamio Arai: gCPG Model for an Autonomous Decentralized Multilegged Robot,h The 4th IFAC Sympo. on Intelligent Autonomous Vehicles, pp. 265~270, 2001.
Takanori Suzuki, Shinkichi
Inagaki, Hideo Yuasa, Tamio Arai: gFault-Tolerance for Autonomous Decentralized
Multi-Legged Robot System,h The 7th International Conf. on Intelligent
Autonomous Systems, pp. 325~332, 2002. ![]()